If you’re exploring how to modernize your material handling operations with automated lifting solutions, you’ve come to the right place. We understand the complexity of integrating lifting beams into automated systems can seem daunting, but with the right approach and expertise, this transformation can revolutionize your operational efficiency and safety standards.
Integrating lifting beams into automated material handling systems involves combining traditional below-the-hook lifting devices with advanced technologies including IoT sensors, AI-driven control systems, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to create intelligent lifting solutions that operate with minimal human intervention. This integration enhances safety, improves efficiency, and reduces operational costs through predictive maintenance and optimized load handling.
TL;DR Summary:
- Lifting beam types and automation compatibility: Fixed, adjustable, and modular spreader bars up to 100-ton capacity work seamlessly with robotic systems and AGVs, requiring ISO-9001 certification and advanced sensor integration
- Efficiency gains and automation benefits: Automated systems deliver 50% handling efficiency increases, 70% labor cost reductions, and 10% decreased carbon emissions through AI-driven optimization
- Integration challenges and solutions: Technical obstacles include infrastructure upgrades, sensor calibration, and cybersecurity requirements, addressed through IIoT platforms and API connections
- Selection criteria for automated systems: Consider load capacity verification, infrastructure compatibility, service level classifications, and predictive maintenance capabilities when choosing equipment
- Safety and compliance standards: ASME B30.20-2026 and OSHA 29 CFR 1926.251 mandate specific requirements including 125% proof testing and comprehensive documentation
- Installation and maintenance best practices: Implement predictive maintenance using AI/ML algorithms, continuous IoT monitoring, and digital twin technology for optimal performance
- Tway Lifting’s specialized solutions: 79 years of American manufacturing excellence providing ISO-9001 certified equipment with same-day production capability and comprehensive support services
Quick Tip: Start your automation journey by conducting a thorough infrastructure assessment—many facilities underestimate the control center, communication system, and maintenance facility upgrades required for successful integration.
As we explore the technical specifications, safety requirements, and implementation strategies throughout this guide, you’ll discover how modern lifting beam integration represents a fundamental shift in material handling philosophy—from reactive manual operations to proactive, data-driven automation that positions your business for long-term success.
What Are Lifting Beams and How Are They Used in Material Handling Automation?
Lifting beams are structural devices that distribute load weight across multiple lifting points in automated material handling systems. The global lifting equipment market reached $84.52 billion in 2024 and projects to $88.33 billion by 2025, driven by smart technology integration including IoT sensors, load monitoring systems, and automated controls.
These specialized beams serve as critical interfaces between crane systems and loads in automated environments. The lifting beams market valued at $725 million in 2024 expects to reach $1.23 billion by 2033 with 5.8% CAGR. Fixed spreader beam markets at $1.5 billion in 2024 project to $2.8 billion by 2033, reflecting strong automation adoption across industries.
The following sections examine compatible beam types, automation-supporting features, and safety standards essential for successful automated integration.
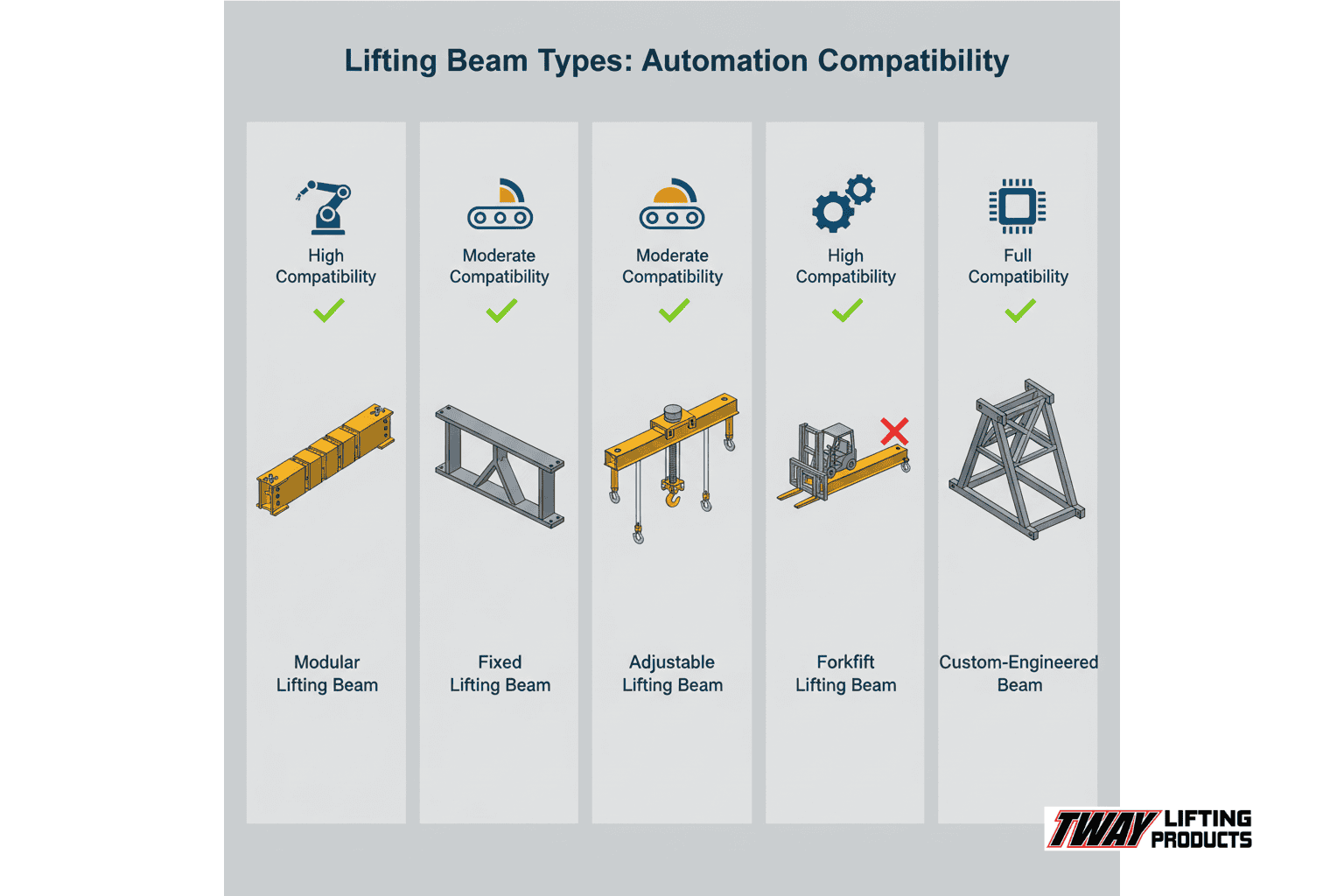
What Types of Lifting Beams Are Compatible with Automated Systems?
The types of lifting beams compatible with automated systems are ISO-9001 certified spreader bars and lifting beams designed for precise automated operations. These include:
- Modular spreader bars: Available up to 100-ton capacity for automated applications
- Fixed spreader bars: Standard configurations for consistent automated lifting patterns
- Adjustable spreader bars: Variable configurations compatible with robotic and AGV systems
- Fork lift beams: Caldwell brand designs that make forklifts more versatile for automated material handling
- Custom-engineered assemblies: Specifically designed lifting solutions for automated general material handling
Each configuration type integrates with different automation technologies, from simple robotic systems to complex AGV networks, ensuring compatibility across diverse automated material handling environments.
What Key Features of Lifting Beams Support Automation?
The key features of lifting beams that support automation are advanced sensor technologies, IoT integration, and digital twin capabilities for predictive operations. Essential automation-supporting features include:
- Advanced sensors: Vibration, temperature, acoustic emission, oil debris, and current signature analysis sensors
- IoT connectivity: Real-time data access and remote monitoring capabilities
- Digital twin technology: Virtual replica creation for predictive modeling and optimization
- Automated tracking: Marked rated load capacity and serial numbers for system integration
- Reliability testing: Hydraulic proof-load testing between 125%-200% of rated capacity
These features enable seamless integration with warehouse management systems, providing continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities essential for uninterrupted automated operations.
What Safety Standards Must Automated Lifting Beam Integrations Meet?
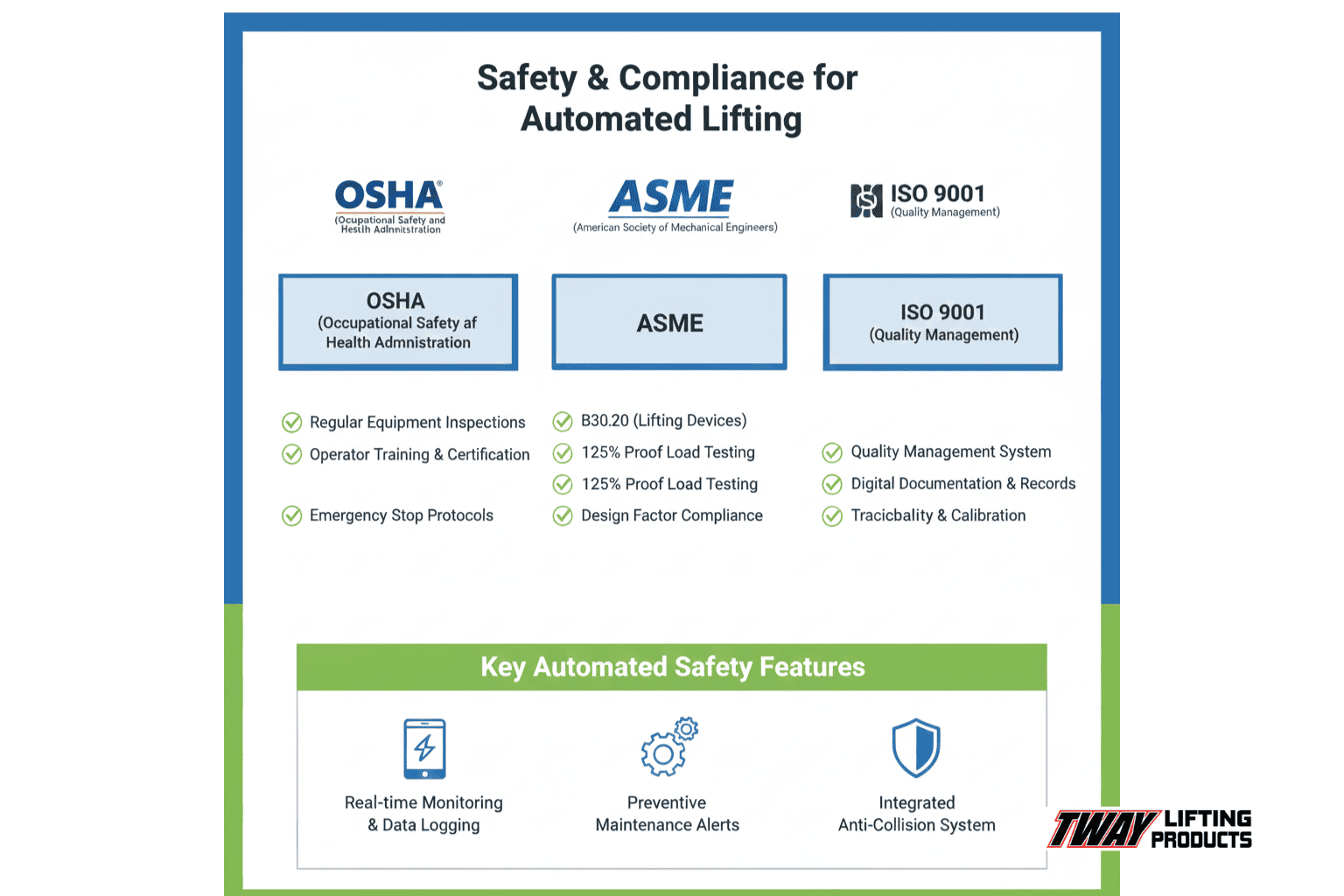
The safety standards that automated lifting beam integrations must meet are ASME B30.20-2026 comprehensive standards for below-the-hook lifting devices and OSHA requirements for automated systems. Critical compliance standards include:
- ASME B30.20-2026: Comprehensive standards for below-the-hook lifting devices
- OSHA 29 CFR 1926.251: Requirements with 125% proof testing for custom-designed lifting accessories
- ASME BTH-1: Design criteria providing minimum structural, mechanical, and electrical specifications
- Nuclear facility protocols: Additional testing requirements and certified material traceability
- Aerospace standards: ISO-9001 certified precision manufacturing requirements
These standards ensure automated lifting operations maintain safety integrity while enabling efficient material handling processes across various industrial applications.
Why Is Integrating Lifting Beams Important for Automated Material Handling Efficiency?
Integrating lifting beams into automated material handling systems increases operational efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances safety across industrial applications. The Shanghai automated container terminal demonstrates this impact with 26 bridge cranes achieving a 50% increase in handling efficiency. Automated systems reduced labor costs by 70% at major port facilities, with expected savings up to $80,000 in terminal operation costs per vessel. Additionally, automated lifting operations deliver a 10% decrease in carbon emissions, supporting sustainability goals while improving productivity.
The integration transforms traditional material handling through enhanced precision, reduced human error, and optimized workflow coordination. Automated lifting beams enable continuous operation with minimal downtime and support predictive maintenance strategies that prevent costly equipment failures.
How Does Automation Change the Role of Lifting Beams?
Automation changes lifting beam operations from manual control to autonomous systems with AI integration and advanced safety features. The shift enables autonomous or remotely controlled systems with AI integration that optimize load handling patterns. Object detection capabilities identify workers or objects to avoid collisions and accidents, creating safer work environments.
Predictive maintenance uses AI/ML algorithms to analyze historical data and predict failures before they occur. Digital twins enable virtual testing of different maintenance strategies without risking equipment downtime. These technologies transform lifting beams from passive tools into intelligent components that actively contribute to system optimization and safety.
What Productivity Benefits Can Businesses Expect from Automated Lifting Beam Use?
Automated lifting beam systems deliver significant productivity gains through enhanced capacity, energy efficiency, and reduced operational complexity. The Port of Melbourne gained additional 33% capacity through automated lifting systems, demonstrating scalable productivity improvements.
Key productivity benefits include:
- Regenerative braking systems capture and reuse energy, reducing overall consumption
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) optimize motor speeds for precise load handling
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) integration enables seamless material handling
- Robotic cranes perform complex tasks with minimal human intervention
These technologies eliminate bottlenecks in material flow while maintaining consistent performance regardless of shift patterns or workforce availability.
How Does Integration Minimize Manual Labor and Errors?
Integration minimizes manual labor and errors by eliminating human factors that contribute to accidents and inefficiencies. Human error accounts for approximately 90% of crane accidents according to safety statistics, making automation a critical safety improvement.
Automated systems eliminate improper communication and poor load planning issues that plague manual operations. Smart cranes detect and prevent potential collisions and overload situations through continuous monitoring. Sway control and automated positioning systems reduce operator error during load placement. Remote operation capabilities keep workers away from hazardous environments while maintaining full operational control.
The combination of these safety features and automated processes creates a work environment where accidents decrease significantly while productivity increases through consistent, optimized performance across all operational cycles.
What Are the Main Challenges When Integrating Lifting Beams with Automation Systems?
Integrating lifting beams with automation systems presents significant obstacles including infrastructure overhauls, AI operational limitations, specialized workforce requirements, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Multiple infrastructure changes are required including control center upgrades, maintenance facility modifications, and communication system enhancements. AI limitations in responding to unprecedented events may cause operations to cease unexpectedly. Companies need technically skilled workers with capabilities in technical engineering, software engineering, and system integration. Cybersecurity risks emerge from computer network or internet-based systems vulnerable to hacking attempts.
The following subsections examine technical obstacles, control system synchronization, and maintenance challenges that organizations must address for successful automation integration.
What Technical Obstacles Must Be Addressed for Seamless Integration?
Technical obstacles in lifting beam automation integration require careful management of sling angles, multi-sensor coordination, and communication protocols. Sling angle effects on load capacity require angles of 30 degrees or greater for safe load distribution, as angles below this threshold can reduce capacity by 50%. Integration of multiple sensor types including vibration, temperature, and acoustic sensors provides a holistic equipment health view but demands sophisticated data processing capabilities.
Key technical challenges include:
- Wireless control systems replacing traditional pendant controls for improved mobility
- Communication protocols between lifting beams and automated control systems
- Calibration requirements for load cells and weight monitoring systems
- Sensor data fusion from diverse monitoring technologies
How Are Control Systems Synchronized Between Lifting Beams and Automation?
Control systems synchronization between lifting beams and automation relies on Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms that provide centralized dashboards for comprehensive monitoring. Automated alerts are configured to trigger when sensor data exceeds predefined thresholds, enabling proactive maintenance responses. Real-time data transmission enables swift decision-making based on the latest operational information.
Synchronization approaches include:
- Integration with warehouse management systems for coordinated material flow
- API connections between lifting equipment and enterprise resource planning systems
- Centralized control interfaces managing multiple lifting operations simultaneously
- Standardized communication protocols ensuring equipment interoperability
What Are Common Troubleshooting or Maintenance Issues?
Common troubleshooting and maintenance issues in automated lifting beam systems stem from inspection failures, sensor degradation, and system compatibility problems. According to a 2019 OSHA analysis, inspection-related failures account for 67% of crane and rigging citations, highlighting the critical importance of maintenance protocols in automated environments.
Primary maintenance challenges include:
- Progressive wear assessment challenges requiring continuous monitoring
- Sensor calibration drift affecting accuracy of automated systems
- Communication interruptions between control systems and lifting equipment
- Software compatibility issues between legacy systems and new automation technology
These challenges demand robust maintenance strategies combining predictive analytics with traditional inspection protocols to ensure safe, reliable automated lifting operations.
How Do You Select the Right Lifting Beam for an Automated Material Handling System?
Selecting the right lifting beam for an automated material handling system requires evaluating capacity, compatibility, and integration requirements. The industrial lifting equipment market valued at $71.79 billion in 2024 indicates wide selection availability, with the heavy lifting equipment market exceeding $25 billion and growing at 5.8% CAGR from 2025 to 2034. Cost considerations range from $250 million AUD for port upgrades to $2.15 billion USD for full terminal automation. This section examines the criteria, assessment methods, and custom solutions needed for optimal lifting beam selection.
What Criteria Should Be Considered When Choosing Lifting Beams for Automation?
The criteria for choosing lifting beams in automated systems include load capacity verification with documented procedures and certified testing facilities. Compatibility with existing infrastructure including control centers and communication systems determines seamless integration. Service level classifications (normal, heavy, severe) determine inspection frequency requirements for automated operations. Environmental conditions and long-term performance validation requirements ensure reliable system function. Integration capabilities with predictive maintenance and monitoring systems enable proactive equipment management.
Additional selection factors include:
- Certified testing documentation for automated tracking
- Communication protocol compatibility with control systems
- Sensor integration capabilities for real-time monitoring
- Compliance with automation safety standards
- Scalability for future system expansion
How Do You Assess Load Requirements and System Compatibility?
Load requirements assessment for automated systems includes design calculations that account for sling angle effects which can reduce capacity by 50% below 30 degrees. Proof testing requirements at 125% of rated load before initial use per OSHA standards verify system integrity. Remaining Useful Life (RUL) estimation through trend analysis of sensor data enables predictive maintenance scheduling. Load monitoring systems with real-time weight verification capabilities provide continuous safety assurance. Structural integrity assessments including crack, deformation, and corrosion evaluation ensure long-term reliability.
System compatibility evaluation requires:
- API compatibility testing with warehouse management systems
- Communication protocol verification between lifting equipment and automation controls
- Sensor calibration validation for accurate load monitoring
- Integration testing with existing safety systems
- Performance validation under automated operating conditions
What Role Do Custom-Engineered Lifting Beams Play in Automation?
Custom-engineered lifting beams play a critical role in automation by addressing unique application requirements that standard beams cannot meet. Custom-designed lifting accessories require 125% proof testing before use per 29 CFR standards with designs completed under qualified engineering supervision per ASME requirements. 3D printing and additive manufacturing enable creation of complex geometries for unique automation needs. Modular designs allow easy customization and adaptation to specific applications with changing requirements. Same-day production capability available for heavy lifting gear through specialized manufacturers reduces downtime during system integration.
Custom solutions provide specific automation benefits such as integrated sensor mounting points, specialized attachment configurations for robotic systems, and enhanced communication capabilities for real-time data transmission. These engineered solutions optimize automated material handling performance while maintaining strict safety and compliance standards throughout the integration process.
What Safety and Compliance Considerations Exist for Automated Lifting Beam Operations?
Safety and compliance considerations for automated lifting beam operations encompass federal regulations, risk assessments, and advanced safety protocols. A 2017 NIOSH analysis of 297 crane-related fatalities from 2011-2017 revealed an annual average of 42-44 deaths in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control, 60% of crane-related fatalities stem from rigging issues, while NIOSH data shows 89% of crane-related fatalities could be prevented through adherence to established safety protocols.
OSHA’s analysis of 249 overhead crane incidents revealed 838 violations resulting in 133 injuries and 133 fatalities. These statistics underscore the critical importance of comprehensive safety measures when integrating automated systems. The following sections detail regulatory compliance requirements, risk assessment protocols, and advanced safety technologies.
How Do OSHA and ASME Standards Impact Automated Integrations?
OSHA and ASME standards establish mandatory compliance frameworks for automated lifting beam integrations with significant financial penalties for violations. OSHA serious violations carry penalties of $15,625 per violation, while willful or repeated violations can reach $156,259 per violation.
Crane operator certification became mandatory nationally on November 10, 2018, requiring recertification every 5 years. The NCCCO program is recognized by federal OSHA as meeting both OSHA and ASME requirements. Documentation requirements include:
- Inspection records with dated signatures
- Proof testing results at 125%-200% capacity
- Maintenance logs with component replacements
- Training certifications for automated system operators
ASME B30.20 standards specifically address below-the-hook lifting devices, requiring comprehensive design documentation and testing protocols for automated integrations.
What Risk Assessments and Safety Protocols Are Involved?
Risk assessments and safety protocols for automated lifting beam operations require systematic evaluation of equipment condition, operational hazards, and emergency procedures. Initial inspection is required before first use to verify compliance with automated system specifications.
Inspection frequencies vary by service classification:
- Daily inspections for severe service environments
- Weekly inspections for heavy service operations
- Monthly inspections for normal service conditions
Periodic annual inspections provide thorough structural integrity assessments including crack detection, deformation analysis, and corrosion evaluation. Risk assessments must evaluate worker exposure during automated operations, considering proximity to moving equipment and emergency egress routes. Emergency response protocols address system failures, power outages, and unexpected events requiring manual intervention.
How Is Worker and Equipment Safety Ensured During Automated Lifting?
Worker and equipment safety in automated lifting operations relies on advanced collision avoidance systems, operator assistance technologies, and comprehensive training programs. Advanced anti-collision systems utilize radar and laser technology for real-time obstacle detection, preventing contact between equipment and personnel.
Operator assistance systems include:
- Sway control minimizing load oscillation
- Load monitoring with weight verification
- Automated positioning for precise placement
- Overload protection preventing capacity exceedance
Virtual Reality training provides immersive simulations in controlled environments, allowing operators to practice emergency procedures without equipment risk. Augmented Reality overlays deliver step-by-step guidance and real-time operational data directly to operator displays. Remote assistance capabilities enable expert support without requiring on-site presence, reducing worker exposure to hazardous environments while maintaining operational expertise.
These technologies work together to create multiple safety barriers, ensuring automated lifting beam operations maintain the highest safety standards while maximizing operational efficiency.
What Are the Best Practices for Installing and Maintaining Lifting Beams in Automated Systems?
The best practices for installing and maintaining lifting beams in automated systems involve comprehensive planning, systematic testing, and continuous monitoring protocols. Successful implementations require development costs ranging from $650 million AUD for facility upgrades to $2.15 billion USD for full automation, with implementation timeframes typically spanning 2-3 years from order placement to operational status. These investments deliver substantial returns through 70% labor cost reduction and 50% efficiency increases across automated material handling operations.
The following sections detail the essential installation procedures, maintenance protocols, and remote monitoring strategies that ensure optimal performance and safety in automated lifting beam systems.
What Steps Should Be Followed During Installation?
Installation steps for automated lifting beam systems begin with comprehensive infrastructure assessment for control center, maintenance facility, and communication system requirements. The process requires proof testing at 125%-200% of rated capacity before deployment, followed by integration testing with automated control systems and safety protocols. Workforce training for technical roles in supervising and maintaining machinery ensures operational readiness, while documentation of all installation procedures and test results provides essential traceability.
Critical installation phases include:
- Site preparation and infrastructure verification
- Equipment positioning and mechanical integration
- Control system programming and calibration
- Safety protocol implementation and verification
- Comprehensive testing under operational conditions
How Is Ongoing Inspection and Maintenance Handled in Automated Settings?
Ongoing inspection and maintenance in automated settings utilizes predictive maintenance using AI/ML algorithms to anticipate failures before occurrence. Continuous monitoring through IoT sensors tracking vibration, temperature, and acoustic emissions provides real-time equipment health data. Automated scheduling of maintenance based on service level classifications ensures optimal uptime, while digital inspection records maintained for full traceability support regulatory compliance and operational transparency.
| Category | Specification | Details | Source |
| Predictive Maintenance | Algorithm Type | AI/ML | Industry Standard 2024 |
| IoT Sensors | Monitoring Parameters | Vibration, Temperature, Acoustics | Technical Specifications |
| Maintenance Schedule | Classification Basis | Service Level | ASME B30.20 |
| Inspection Records | Format | Digital | OSHA Requirements |
| Rental Equipment | Re-inspection | Before Every Dispatch | Safety Protocols |
This automated approach transforms traditional reactive maintenance into proactive system optimization, reducing unexpected downtime and extending equipment lifecycle.
How Can Remote Monitoring Enhance Safety and Performance?
Remote monitoring enhances safety and performance through real-time monitoring of crane performance from central locations. Automated alerts trigger when sensor data exceeds predefined thresholds, enabling immediate response to potential issues. Remote diagnostics facilitate timely troubleshooting without site visits, while continuous data analysis identifies operational bottlenecks and optimization opportunities. Cloud-based platforms enable collaboration between maintenance, operations, and engineering teams for coordinated system management.
The integration of these remote monitoring capabilities creates a comprehensive safety and performance framework that minimizes risks while maximizing operational efficiency through data-driven decision making.
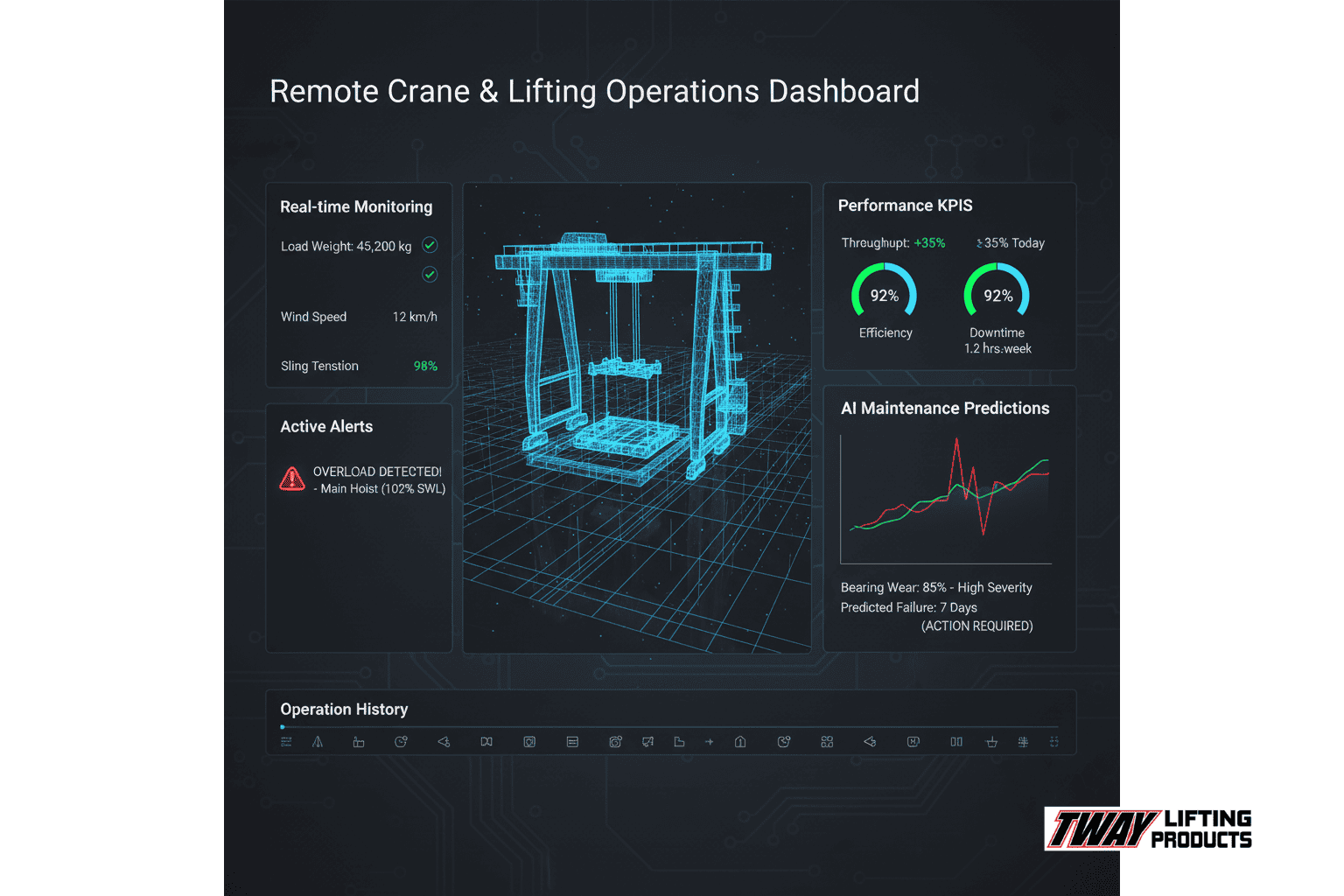
How Should You Approach Integrating Lifting Beams into Automated Systems with Tway Lifting?
Integrating lifting beams into automated systems requires a strategic partnership approach that combines technical expertise with proven manufacturing capabilities. Tway Lifting brings 79 years of American manufacturing excellence to automation integration projects, operating from facilities in Indianapolis and Fort Wayne, Indiana, including their specialized Wire Rope Products Plant. Their ISO-9001 certified spreader bars and lifting beams manufacturing ensures compliance with automation system requirements, while same-day production capability addresses urgent project timelines.
Successful automation integration depends on three critical factors: technical compatibility, safety compliance, and reliable support infrastructure. The following sections detail how Tway Lifting addresses each requirement through specialized services and partnerships.
Can Tway Lifting Help Streamline the Integration of Lifting Beams into Automated Material Handling?
Yes, Tway Lifting can streamline automation integration through their comprehensive manufacturing and support services. As a full-service manufacturer and distributor, they provide custom fabrication services tailored to specific automated system requirements. Their professional pull testing services verify automated system components meet OSHA’s 125% proof testing requirements before deployment.
Their rental program features serialized equipment with Certificate of Test and inspection records, enabling rapid deployment while maintaining full compliance documentation. Digital inspection records provide complete traceability essential for automated systems, while partnerships with leading automation technology providers including Crosby Group and GrabiQ ensure seamless integration with existing control systems.
This streamlined approach reduces project timelines and eliminates compatibility issues common in multi-vendor automation installations.
What Are the Key Takeaways About Integrating Lifting Beams into Automated Material Handling Systems?
The key takeaways center on market growth, planning requirements, proven ROI, regulatory compliance, and strategic partnerships. Market growth at 5.8% CAGR indicates strong industry adoption of automated lifting solutions, validating investment decisions in automation technology.
Integration requires comprehensive planning including infrastructure upgrades, workforce training, and safety protocol development. ROI is achieved through documented 70% labor reduction and 50% efficiency gains in successful implementations. Compliance with ASME B30.20 and OSHA standards remains non-negotiable for legal operation, regardless of automation level.
Partner selection proves critical, with providers like Tway Lifting offering 70+ years of experience and comprehensive support services. Their established track record in both traditional and automated applications provides the technical foundation necessary for successful long-term automation integration projects.