If you’re exploring ISO-9001 certification for your lifting equipment manufacturing operations, you’re likely seeking ways to enhance safety, improve quality control, and expand market opportunities. Understanding this internationally recognized standard and its specific applications in the lifting equipment sector can help you make informed decisions about certification. This guide provides comprehensive insights into how ISO-9001 transforms manufacturing operations and creates competitive advantages.
ISO-9001 certification in lifting equipment manufacturing is an internationally recognized quality management system standard that ensures consistent product quality, safety compliance, and operational excellence through documented processes, continuous improvement, and third-party verification. In 2024, the North American ISO certification market reached USD 4.1 billion with 13.2% CAGR growth, indicating strong industry adoption (Cognitive Market Research, 2024). According to T.S. Kathayat, President of Corporate Quality at Welspun Corp Ltd, 2018: “ISO 9001 helped us establish our corporate quality management system globally throughout our facilities… Within months, our plant garnered the approval of many Fortune 100 oil and gas companies.”
ISO-9001 certification importance for manufacturers centers on safety improvements achieving 22.6% accident frequency reduction, financial benefits delivering 15-25% higher Return on Capital Employed, and market access requirements from Fortune 100 corporations. Risks without certification include 20% lower Return on Assets, exclusion from major supply chains, and higher workplace incidents. Main requirements encompass documented Quality Manual creation, process flowchart mapping, PDCA cycle implementation, risk-based thinking adoption, and leadership commitment demonstration. The certification process involves gap analysis conducting, documentation developing, internal audits performing, management reviews executing, and two-stage certification audits completing within 3-12 months. Regulatory compliance strengthens through ISO-9001’s alignment with OSHA 1910.179 crane standards, 1926.251 rigging requirements, and 1910.184 sling regulations. Customer benefits include third-party quality validation, consistent product reliability, enhanced supplier credibility, and contract prerequisite fulfillment. Certification maintenance requires annual surveillance audits, three-year recertification cycles, continuous improvement demonstrations, and corrective action implementations. For manufacturers seeking certification support, Tway Lifting offers ISO-certified expertise performing hydraulic proof testing up to 110 tons, maintaining professional welder certifications, and supplying stadium construction projects nationwide.
Focus on establishing robust documentation systems early in your certification journey, as these form the foundation for sustainable quality management and regulatory compliance.
Your ISO-9001 certification journey represents a strategic investment in operational excellence, safety leadership, and market competitiveness that positions your lifting equipment manufacturing operations for long-term success in an increasingly quality-conscious global marketplace.
Why Is ISO-9001 Certification Important for Lifting Equipment Manufacturers?
ISO-9001 certification is important for lifting equipment manufacturers because it establishes quality management systems that reduce accidents, improve financial performance, and open access to major contracts. Certified manufacturers demonstrate systematic approaches to quality that protect workers and enhance business competitiveness. This certification creates measurable safety improvements while positioning companies for growth in demanding industrial sectors.
How Does ISO-9001 Certification Improve Product Quality and Safety?
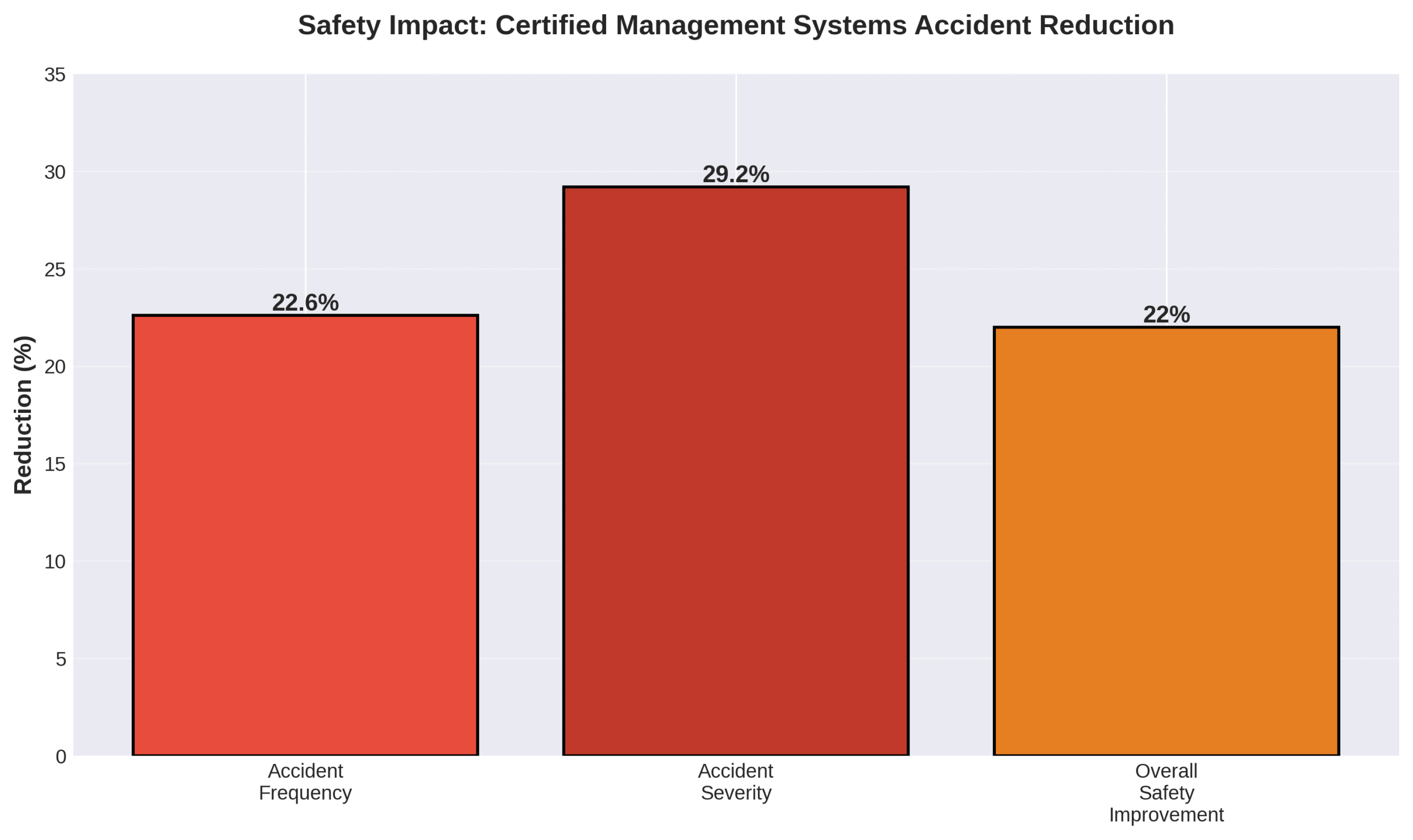
ISO-9001 certification improves product quality and safety by establishing structured quality management systems that systematically reduce workplace accidents and enhance manufacturing reliability. Companies with certified safety management systems experience a 22.6% decrease in accident frequency and a 29.2% decrease in accident severity, according to industrial safety research.
The structured QMS framework mandated by ISO 9001 creates safer manufacturing environments through:
- Formal documentation requirements for all critical processes
- Regular training protocols for personnel handling lifting equipment
- Systematic inspection procedures that catch defects before products reach customers
- Risk-based thinking that identifies potential hazards proactively
These formal quality management systems directly improve product reliability and safety metrics by standardizing manufacturing processes and requiring continuous monitoring of quality indicators throughout production cycles.
What Are the Risks of Operating Without ISO-9001 Certification?
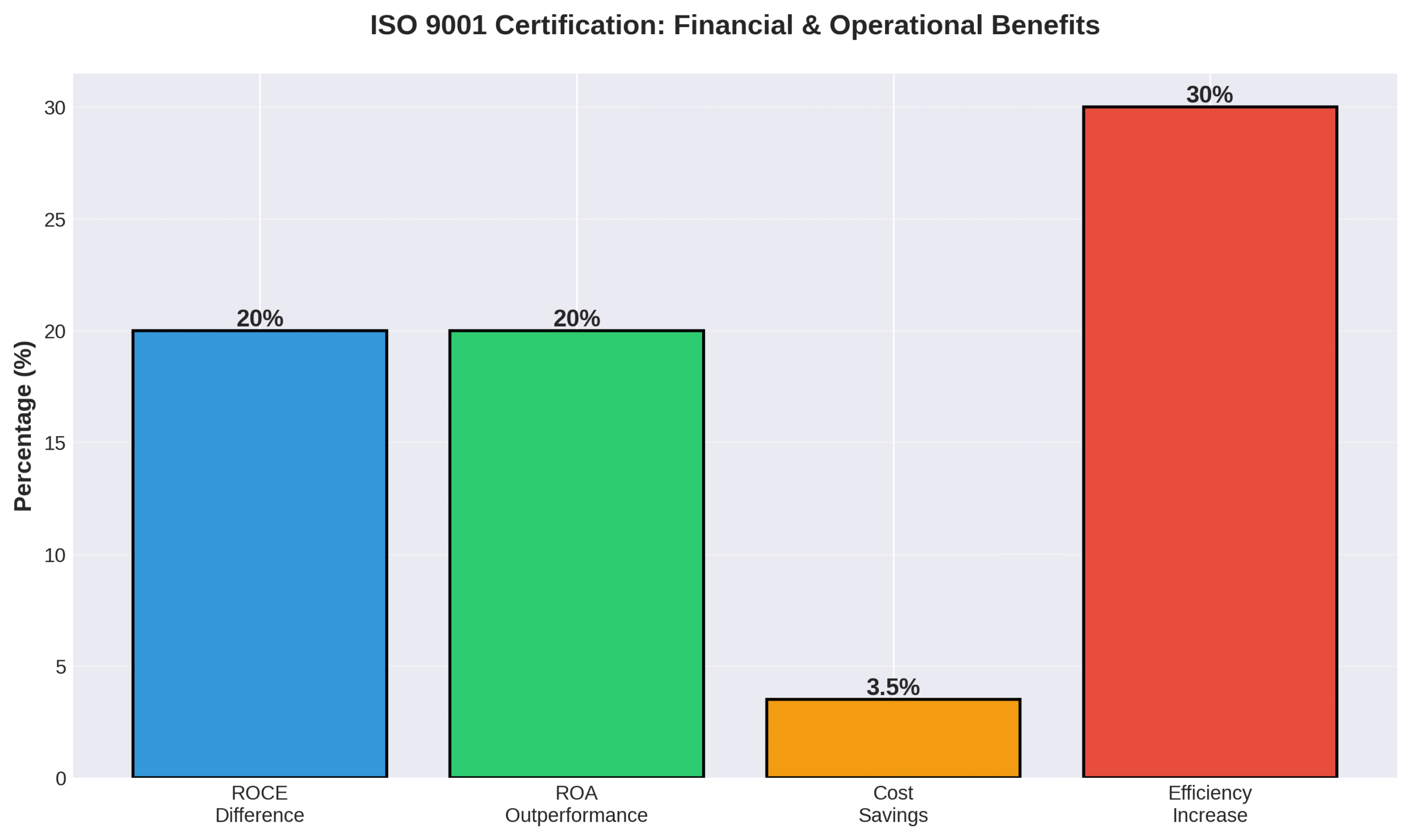
The risks of operating without ISO-9001 certification include significant financial underperformance and limited market access that can restrict business growth. Non-certified companies have Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) that is 15-25% lower than certified competitors, while their Return on Assets (ROA) underperforms by over 20% compared to certified firms.
Operating without certification creates these specific business risks:
- Contract limitations: Exclusion from major contracts in oil, gas, construction, and automotive sectors
- Supply chain restrictions: Fortune 100 corporations often require certification for supplier qualification
- Safety liability: Higher accident rates and safety incidents increase insurance costs and legal exposure
- Competitive disadvantage: Inability to compete for high-value projects requiring quality assurance documentation
These risks compound as industrial customers increasingly demand third-party quality validation from their lifting equipment suppliers, making certification essential for sustained market participation.
What Are the Main Requirements for ISO-9001 Certification in Lifting Equipment Manufacturing?
ISO-9001 certification for lifting equipment manufacturers requires comprehensive quality management systems, documented processes, and adherence to seven core quality principles. These requirements ensure consistent product quality, regulatory compliance, and systematic operational control across all manufacturing activities.
What Processes Must Be Documented to Achieve Compliance?
The processes that must be documented for ISO-9001 compliance include quality manuals, manufacturing procedures, inspection records, and training documentation. Lifting equipment manufacturers must maintain a Quality Manual documenting the entire quality management system alongside detailed policies and procedures for all manufacturing processes. Process flowcharts mapping production workflows provide visual documentation of operational sequences, while written certification records for monthly inspections align with OSHA requirements for crane and hoist safety.
Additional documentation requirements include:
- Equipment modification and maintenance activity records
- Training records demonstrating personnel competence for welders and inspectors
- Internal audit reports validating system effectiveness
- Management review documentation showing continuous improvement efforts
According to OSHA 1910.179 requirements, manufacturers must maintain systematic documentation for overhead crane inspections, which ISO-9001’s documentation framework directly supports through structured record-keeping protocols.
Which Quality Management Principles Are Essential for Certification?
The quality management principles essential for ISO-9001 certification are process approach, PDCA cycles, risk-based thinking, customer focus, leadership commitment, evidence-based decisions, and continual improvement. The process approach focuses on systematic workflow management, ensuring each manufacturing step connects logically to achieve consistent lifting equipment quality. PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle implementation throughout operations creates structured problem-solving and improvement methodologies.
Risk-based thinking, introduced in the ISO 9001:2015 revision, requires manufacturers to identify potential hazards in lifting equipment production and implement preventive measures. Customer focus serves as the primary organizational driver, while leadership commitment at all organizational levels ensures quality objectives receive adequate resources and attention.
The remaining principles include evidence-based decision making using documented data from inspections and testing, plus continual improvement embedded in daily operations. A 2019 manufacturing safety study found that companies implementing these seven principles experienced a 22.6% decrease in accident frequency and 29.2% decrease in accident severity compared to non-certified manufacturers.
These requirements establish the foundation for successful ISO-9001 certification, preparing manufacturers for the detailed certification process that follows.
How Does the ISO-9001 Certification Process Work for Lifting Equipment Manufacturers?
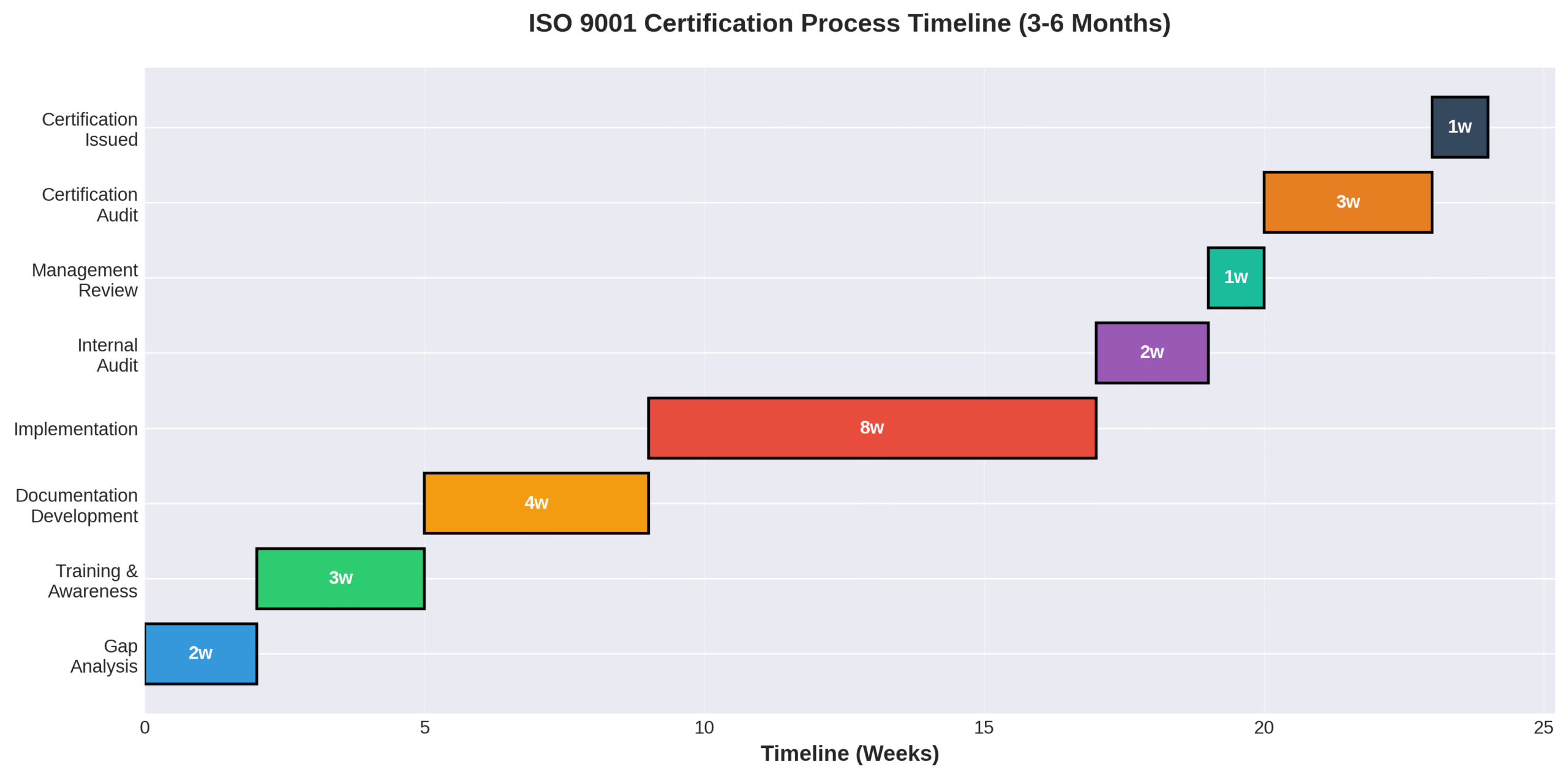
The ISO-9001 certification process for lifting equipment manufacturers follows a structured eight-step approach designed to establish and validate quality management systems. This comprehensive process transforms manufacturing operations through systematic implementation of quality controls and documentation standards.
The certification journey begins with gap analysis and concludes with formal certification, typically spanning 3-12 months depending on organizational complexity. Each phase builds upon previous steps to ensure thorough QMS integration before external audit validation.
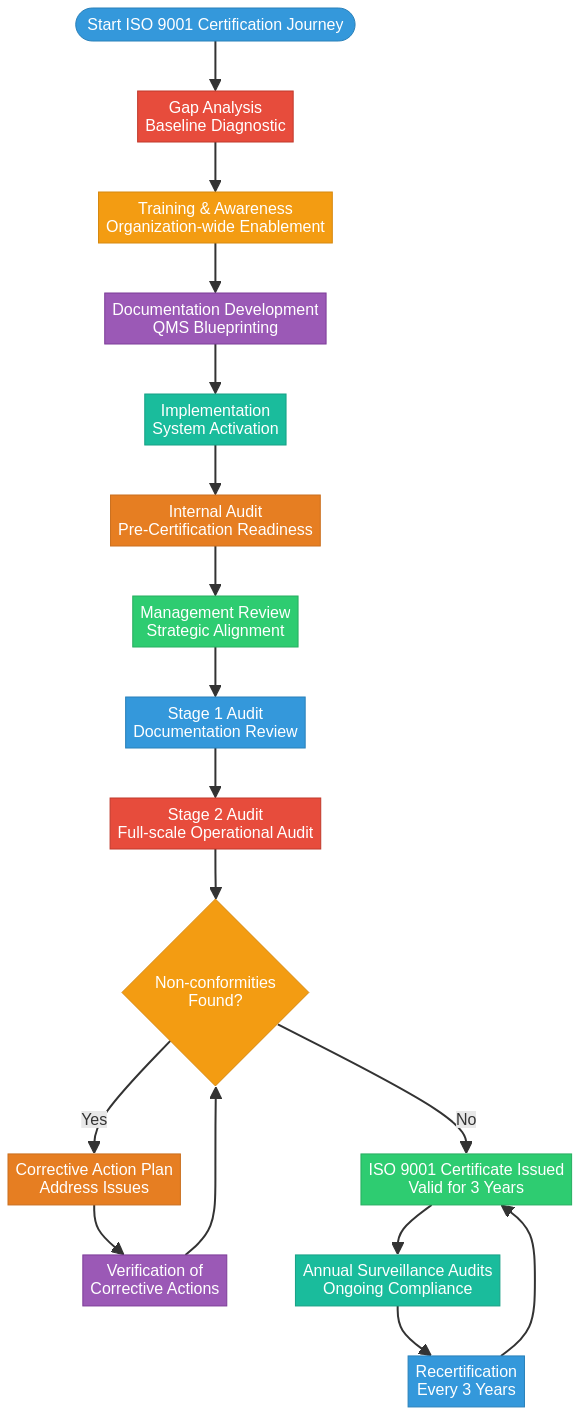 What Are the Steps Involved in Preparing for ISO-9001 Certification?
What Are the Steps Involved in Preparing for ISO-9001 Certification?
The steps involved in preparing for ISO-9001 certification are gap analysis, training, documentation development, implementation, internal audit, management review, certification audit, and final certification.
The process begins with gap analysis—an initial diagnostic review benchmarking existing quality management systems against ISO 9001:2015 requirements. This assessment identifies specific areas requiring development or enhancement.
Training and awareness programs educate stakeholders on core ISO 9001 principles, ensuring organization-wide understanding of quality management concepts. Documentation development creates the Quality Manual, policies, procedures, and process flowcharts that form the QMS foundation.
Implementation integrates new QMS policies into daily operations, followed by internal audits that validate implementation readiness through formal assessment protocols. Management review provides strategic assessment by executives of QMS performance and audit findings.
The certification audit involves a two-stage process by an accredited Certification Body: Stage 1 conducts documentation review while Stage 2 performs operational audit. Final certification occurs when the ISO 9001 certificate is issued upon successful resolution of any identified non-conformities.
How Long Does the Certification Process Typically Take?
The certification process typically takes 3 to 12 months, with timeline variations based on organizational size and complexity.
Small companies may complete certification in 3-6 months due to streamlined operations and fewer processes requiring documentation. Large or complex organizations often require 9-12 months to address extensive manufacturing systems and multi-facility coordination challenges.
Timeline factors include company size, industry complexity, and scope of certification across different product lines or manufacturing locations. The preparation phase including gap analysis typically requires 1-3 months for thorough assessment and planning.
Implementation and internal audit phases span 2-6 months, allowing sufficient time for process integration and validation. Certification audit scheduling adds 1-2 months to the overall timeline due to certification body availability and audit complexity requirements.
What Are Common Challenges Faced During Certification?
Common challenges faced during certification are securing management commitment, overcoming resistance to change, balancing documentation requirements, fostering quality culture, allocating resources, maintaining momentum, and addressing non-conformities.
Securing genuine management commitment throughout the organization proves challenging when leadership fails to demonstrate consistent support for quality initiatives. Overcoming resistance to change occurs due to employee fear and misperceptions about ISO requirements creating additional bureaucracy.
Balancing documentation requirements without creating unnecessary paperwork demands careful planning to maintain operational efficiency. Fostering a quality culture across all departments and levels requires sustained effort to change ingrained behaviors and attitudes.
Resource allocation challenges include dedicating sufficient personnel time and financial investment for implementation and comprehensive training programs. Maintaining momentum during the lengthy certification process becomes difficult when daily operational pressures compete with quality system development priorities.
Addressing non-conformities identified during certification audits requires prompt corrective action planning and implementation to achieve successful certification outcomes.
This systematic certification approach establishes the foundation for ongoing quality management excellence, preparing manufacturers for the next phase of maintaining compliance with regulatory standards and customer expectations.
How Does ISO-9001 Certification Affect Compliance with US Industry Regulations?
ISO-9001 certification significantly enhances compliance with US industry regulations by creating systematic documentation and process controls that align with federal safety standards. The certification establishes a quality management framework that directly supports OSHA requirements and other regulatory mandates in lifting equipment manufacturing.
How Does ISO-9001 Relate to OSHA and Other Regulatory Standards?
ISO-9001 relates to OSHA standards through complementary documentation and process requirements that reinforce safety compliance. The standard’s documentation requirements directly support OSHA 1910.179 compliance for overhead and gantry cranes, while process controls align with OSHA 1926.251 requirements for rigging equipment inspection.
Key regulatory alignments include:
- Training mandates that support OSHA’s designated personnel requirements for equipment operation
- Risk-based thinking from ISO 9001:2015 that helps prevent OSHA safety violations
- Compliance facilitation for OSHA 1926.1441 covering equipment with 2,000+ pound lifting capacity
- QMS framework addressing OSHA 1910.184 requirements for sling inspection documentation
- Systematic safety approach that aligns with OSHA’s overall compliance framework
The integration creates a unified approach where ISO-9001 quality processes reinforce regulatory safety requirements across lifting equipment operations.
What Documentation Is Required for Regulatory Audits?
The documentation required for regulatory audits encompasses both ISO-9001 quality records and OSHA-mandated safety documentation. Written certification records for monthly crane and hoist inspections satisfy OSHA requirements while supporting ISO-9001 process documentation standards.
Essential audit documentation includes:
- Equipment modification documentation and comprehensive maintenance logs
- Personnel training and competence records for operators and inspectors
- Process control documentation for manufacturing and inspection procedures
- Risk assessment documentation supporting proactive hazard prevention strategies
- Internal audit reports demonstrating ongoing compliance monitoring activities
- Management review records showing continuous improvement efforts
This documentation framework serves dual purposes by satisfying both quality management certification requirements and federal regulatory compliance obligations, creating efficiency in audit preparation and regulatory oversight.
What Benefits Do Customers and Partners Gain from a Manufacturer’s ISO-9001 Certification?
ISO-9001 certification delivers substantial benefits to customers and partners by providing third-party validation of quality standards and opening access to premium markets. Certified manufacturers demonstrate consistent product quality that builds trust with buyers and enables participation in high-value supply chains.
How Does Certification Impact Buying Decisions for Lifting Equipment?
Certification impacts buying decisions by providing quality assurance that influences contract awards and market access. The ISO “badge of quality” opens doors to new customers and overseas markets, while buyers view ISO 9001 as evidence of consistent product quality and reliability.
More customers are requiring ISO 9001 certification as a prerequisite for contracts. The North American ISO certification market valued at USD 4.1 billion in 2024, growing at 13.2% CAGR, reflects increasing demand for certified suppliers. Certification enables participation in supply chains of Fortune 100 oil and gas companies and is often required for bidding on large construction and infrastructure projects.
Buyers gain confidence through third-party validation of quality and safety standards. Certification provides documented evidence that manufacturers maintain systematic quality management processes, reducing procurement risk for customers investing in lifting equipment.
Does ISO-9001 Certification Enhance Supplier Relationships?
ISO-9001 certification enhances supplier relationships by establishing credibility and enabling access to demanding market sectors. Welspun Corp gained approval from Fortune 100 oil and gas companies within months of certification, demonstrating the immediate relationship benefits certification provides.
ISO 9001 helps establish corporate quality management systems globally across facilities. Tway Lifting Products became the only ISO-certified rigging manufacturer in their region, creating competitive advantage. CEO Peter Hansen states: “We’re finding that more and more of our customers are requiring certification.”
Certification demonstrates commitment to accuracy and consistency as companies grow. ISO 9001 enables manufacturers to win contracts for high-profile projects such as Lucas Oil Stadium and AT&T Stadium. The certification builds credibility needed to compete in demanding global energy sectors and establishes long-term partnership foundations with major industrial customers.
The next section examines how manufacturers can maintain their ISO-9001 certification over time through ongoing audits and continuous improvement practices.
How Can Manufacturers Maintain Their ISO-9001 Certification Over Time?
ISO-9001 certification maintenance requires ongoing commitment to quality management system compliance and continuous improvement practices. Manufacturers must navigate recurring audit cycles while sustaining performance improvements that justify their initial certification investment.
What Are the Ongoing Audit and Recertification Requirements?
The ongoing audit and recertification requirements include annual surveillance audits and triennial full recertification cycles. ISO 9001 certificates remain valid for three years from initial issuance, during which manufacturers must demonstrate continuous compliance with all ISO 9001:2015 requirements through scheduled surveillance audits conducted by Certification Bodies.
Annual surveillance audits evaluate specific QMS elements to verify ongoing conformity. Organizations must address non-conformities identified during these audits within specified timeframes and provide documentation of corrective actions for audit closure. Full recertification audits occur every three years, requiring comprehensive review of the entire quality management system.
Certification Bodies may conduct unscheduled audits when significant changes occur in manufacturing processes, facility locations, or organizational structure. This audit framework ensures sustained compliance with ISO standards while maintaining the integrity of the certification process.
How Can Continuous Improvement Be Sustained After Certification?
Continuous improvement can be sustained through systematic implementation of the PDCA cycle and regular performance monitoring against measurable objectives. The continual improvement principle embedded in the ISO 9001 framework drives ongoing enhancements that yield measurable business results.
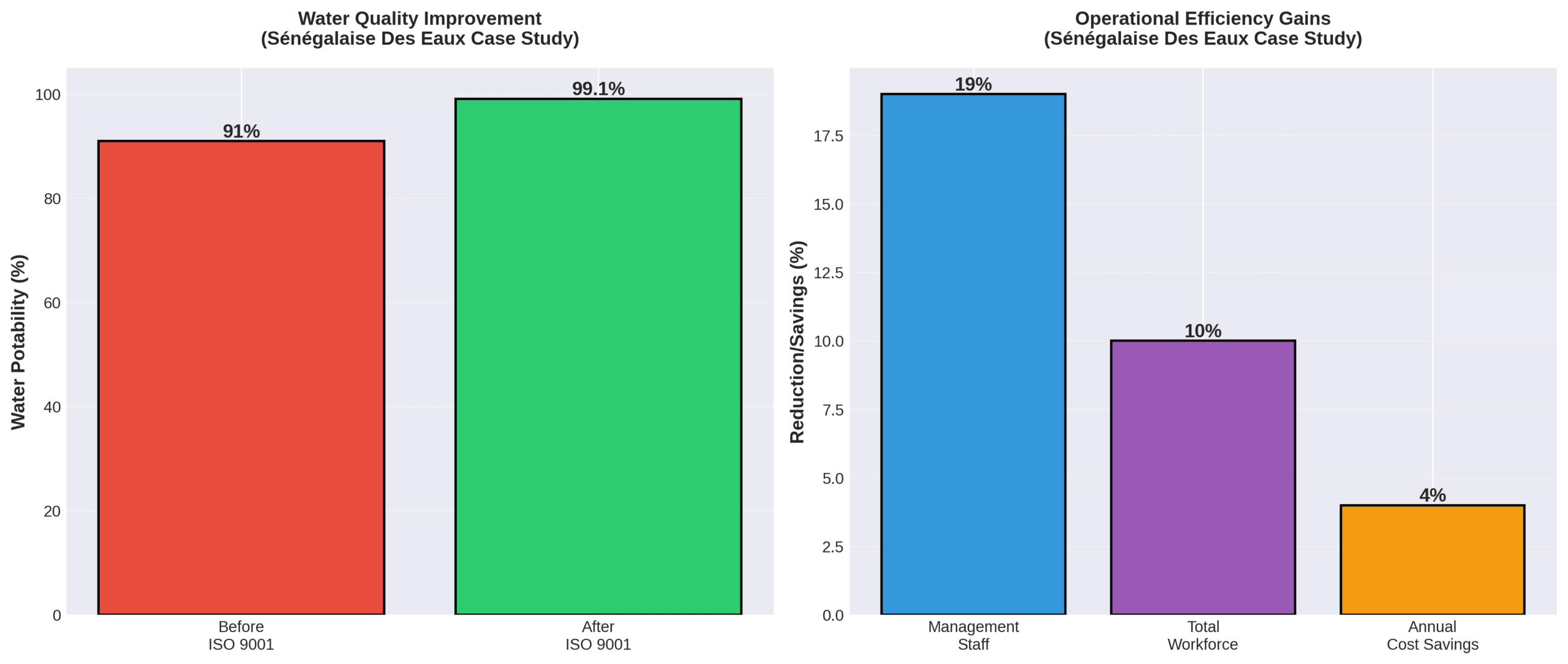
A 2021 study on water utilities revealed that Sénégalaise Des Eaux achieved 99.1% water potability, up from 91%, through continuous improvement initiatives. Companies report average annual cost savings of 4% over five years post-certification, with ISO 9001 enabling a 19% reduction in managerial staff through efficiency gains and nearly 10% workforce optimization through enhanced productivity.
 Regular internal audits identify opportunities for process enhancement while management reviews assess QMS performance against established objectives. These systematic approaches maintain momentum for improvement initiatives and support long-term certification value.
Regular internal audits identify opportunities for process enhancement while management reviews assess QMS performance against established objectives. These systematic approaches maintain momentum for improvement initiatives and support long-term certification value.
The structured approach to maintaining certification creates a foundation for sustained operational excellence that extends well beyond initial compliance requirements.
Ready to Strengthen Your Operations with Certified Lifting Equipment Rental?
Tway Lifting’s ISO-certified operations ensure that every piece of lifting and rigging equipment available for rent meets strict quality and safety standards. As a trusted name in the industry since 1945, Tway applies the same ISO-9001 principles used in its manufacturing and testing processes to its rental division—delivering reliability, compliance, and peace of mind for your next project.
Can You Rent ISO-Certified Lifting Equipment from Tway Lifting?
Yes, you can rent ISO-certified lifting equipment from Tway Lifting. Our Lifting Equipment Rental Services provide rigorously tested and certified slings, chains, hoists, and rigging gear maintained under the same ISO 9001 quality management system that governs our manufacturing and inspection processes. Each rental item undergoes hydraulic proof load testing, visual inspection, and full documentation to ensure traceability and compliance with OSHA and ASME standards. Whether your project requires short-term lifting solutions or long-term equipment rentals, Tway delivers safe, certified, and reliable equipment backed by decades of quality assurance expertise.
Is ISO-9001 Certification Important for Lifting Equipment Rentals?
Absolutely. ISO-9001 certification guarantees that every rental process—from inspection to delivery—follows verified quality standards, ensuring equipment performance and user safety. For customers, this means fewer on-site risks, consistent reliability, and equipment that’s fully compliant with federal and industry regulations. Tway Lifting’s certified systems extend beyond production—they support every rental client with the same level of operational excellence that defines our manufacturing and testing services.
What Are the Key Takeaways About ISO-9001 Certification in Lifting Equipment Manufacturing?
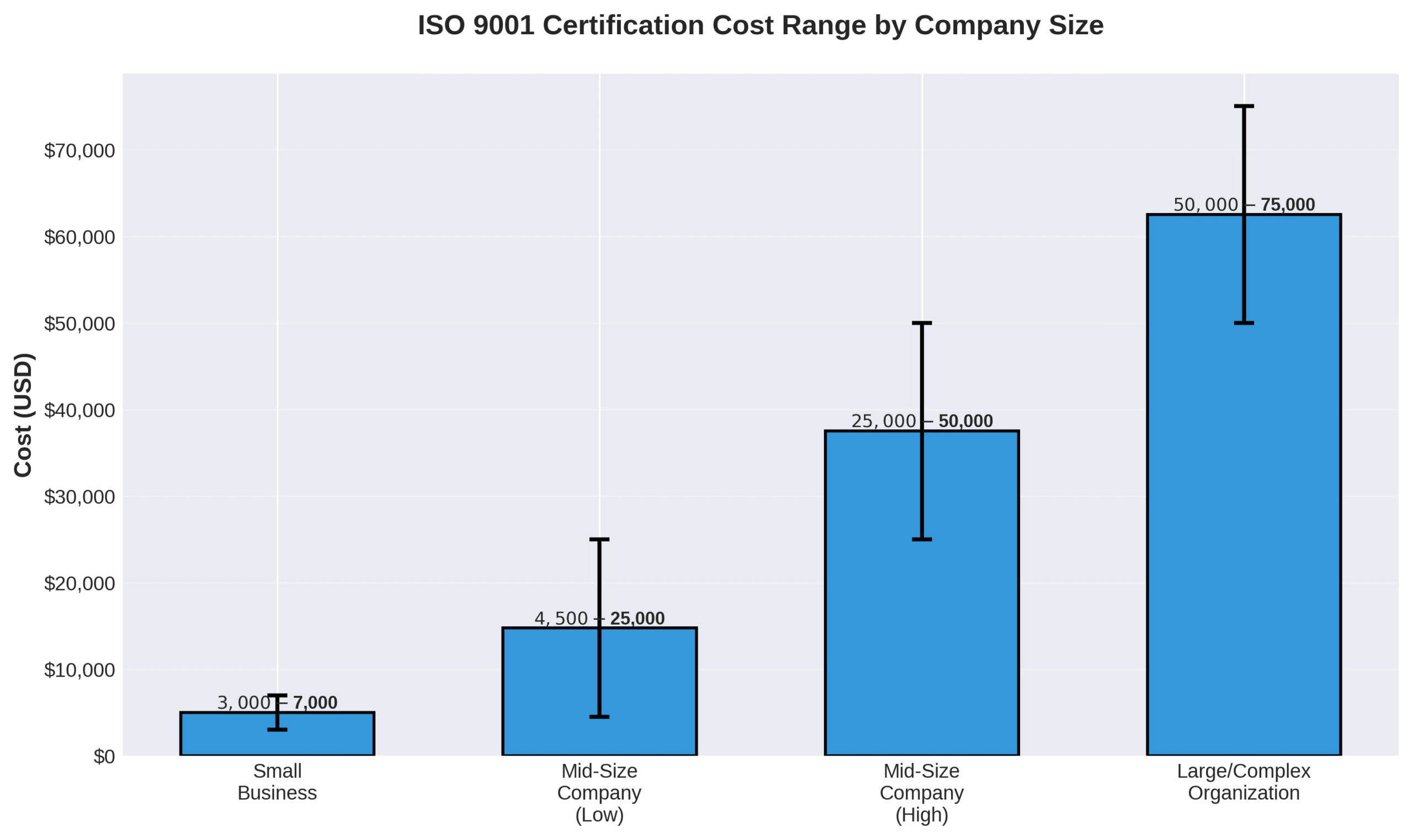
The key takeaways about ISO-9001 certification in lifting equipment manufacturing center on strategic investment returns and operational improvements. Initial certification costs range from $3,000-$7,000 for small businesses to over $75,000 for large organizations.
Financial Performance Benefits:
- ISO 9001 certification yields 15-25% higher Return on Capital Employed versus non-certified companies
- Certified companies show over 20% better Return on Assets performance
- Strategic investment opens global markets and enhances competitive positioning
Safety and Operational Improvements:
- Implementation reduces accident frequency by 22.6% and severity by 29.2%
- Certification process typically requires 3-12 months depending on organizational complexity
- ISO 9001 creates framework supporting OSHA compliance and regulatory requirements
These metrics demonstrate that certification delivers measurable returns through improved safety performance, operational efficiency, and market access for lifting equipment manufacturers.