You’re here because you need to understand load testing equipment for lifting gear certification—whether you’re ensuring workplace safety compliance, selecting testing equipment for your facility, or preparing for upcoming inspections. We’ll guide you through everything you need to know about the equipment, standards, and best practices that keep lifting operations safe and compliant across the United States.
Load testing equipment for lifting gear certification is specialized machinery that applies controlled force to verify the structural integrity and operational safety of cranes, hoists, slings, and other lifting devices before workplace use. This equipment ranges from water-filled bags and hydraulic load cells to traditional solid test weights, each serving specific testing needs based on capacity requirements, portability constraints, and accuracy standards. At Tway Lifting, we’ve been helping American businesses navigate these critical safety requirements since 1945, providing both the equipment and expertise needed for comprehensive lifting gear certification.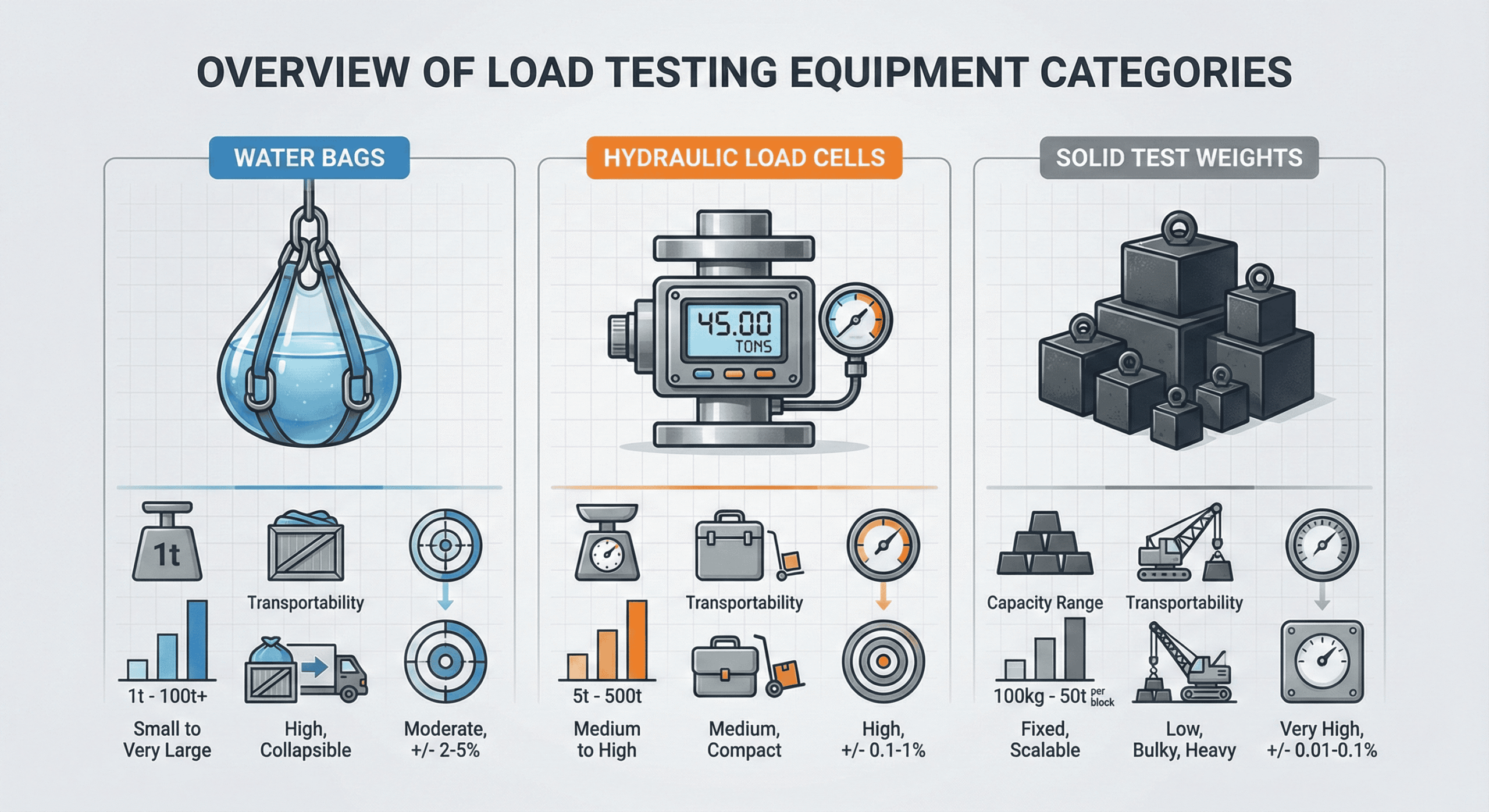
TL;DR Summary:
- Load testing validates lifting gear safety through controlled force application, preventing 80% of capacity-related accidents and ensuring $6 ROI per $1 invested in safety
- Main equipment categories include water bags (1-110 tonnes), hydraulic load cells (1-1,500 tonnes with ±1% accuracy), and ASTM-certified solid test weights
- Legal requirements mandate testing before initial use and every 4 years per OSHA 1910.179, with penalties up to $156,259 for violations
- Equipment selection depends on factors like rated capacity, transportability needs, environmental conditions, and industry-specific requirements
- Best practices include annual calibration, proper environmental protection, and maintaining comprehensive documentation throughout equipment lifespan
- Professional providers like Tway Lifting offer comprehensive solutions including equipment supply, rental services, and hydraulic testing up to 220,000 lbs
Quick Tip: When selecting load testing equipment, prioritize gradual load application methods like water bags over sudden-impact solid weights to minimize equipment stress and extend service life—this gentle approach can significantly reduce the risk of structural damage during testing while maintaining compliance with all regulatory standards.
Why Is Load Testing Essential for Lifting Gear Certification?
Load testing ensures lifting equipment meets safety standards and prevents workplace accidents through systematic verification of structural integrity. This process applies controlled loads to verify equipment can safely handle rated capacities before operational use.
Load testing validates safety compliance by applying controlled force to lifting equipment, verifying structural integrity and operational safety before workplace use. The process uses specialized procedures, equipment-specific protocols, and standardized guidelines to ensure safety compliance. According to industry data, 80% of crane accidents result from exceeding equipment capacity, while proof-loading prevents 80% of capacity-related accidents through systematic verification. Testing ensures $6 ROI per $1 invested in safety, and 60% of fatal crane injuries involving struck-by incidents link to falling materials.
The next sections examine specific legal requirements and compliance standards that govern load testing procedures.
How Does Load Testing Validate Lifting Gear Safety and Compliance?
Load testing validates safety compliance by applying controlled force to lifting equipment and verifying structural integrity before operational use. This systematic process uses specialized procedures, equipment-specific protocols, and standardized guidelines to prevent equipment failure during critical lifting operations.
Statistical evidence demonstrates load testing’s effectiveness in preventing accidents. Proof-loading prevents 80% of capacity-related accidents through systematic verification, while 80% of crane accidents result from exceeding equipment capacity. Testing ensures a $6 return on investment per $1 invested in safety measures. Additionally, 60% of fatal crane injuries involving struck-by incidents link to falling materials from improperly tested equipment.
Load testing serves as the final verification step before equipment enters service, establishing baseline performance parameters and identifying potential structural weaknesses that could lead to catastrophic failures.
What Are the Legal and Regulatory Requirements for Load Testing in the US?
The legal requirements for load testing in the US center on OSHA regulations that mandate specific testing protocols for different lifting equipment types. OSHA 29 CFR 1910.179 serves as the core regulation governing overhead and gantry cranes, mandating load testing for new and altered cranes with specific capacity and frequency requirements.
Key OSHA Requirements:
- Test loads must not exceed 125% of rated capacity unless manufacturer specifies otherwise
- Operational load rating should not exceed 80% of maximum test load
- Existing crane and hoist systems require load testing at minimum once every four years
- OSHA 1919.71 requires unit proof tests of cranes before initial use and every 4 years thereafter
Current OSHA Penalties (as of January 15, 2025):
- Serious violations: $14,502 maximum
- Failure to abate: $14,502 per day beyond deadline
- Repeat/willful violations: $156,259 maximum per violation
OSHA issued a $5,795 fine in 2017 for manual pallet jack non-compliance with rated load posting requirements. CMAA Specification 78 requires written reports to be kept for entire equipment lifespan, with test reports filed and accessible to authorized personnel throughout the equipment’s operational life.
What Are the Main Categories of Load Testing Equipment for Lifting Gear?
Load testing equipment is divided into two primary categories based on application method: static load testing equipment and dynamic load testing equipment. These categories serve different testing requirements mandated by OSHA regulations and industry standards for lifting gear certification.
The following sections examine the specific equipment types within each category and their operational characteristics.
Which Equipment Is Commonly Used for Static Load Testing?
Static load testing equipment applies 125% of rated capacity for 10 minutes while holding the load 4 inches off the ground to assess structural integrity and check for permanent deformation.
Water bags provide the most versatile static testing solution:
- Capacity range from 1 to 110 tonnes with gradual load application
- Gradual loading prevents sudden stress compared to solid weights
- Lightweight transport capability via pickup truck for 100-ton tests
- Proofload specifications allow testing up to 1,000 tons with spreaders
Hydraulic load cells deliver precision measurement:
- Measure both static and tension loads within ±1% accuracy of full scale
- Available capacity range from 1 to 1,500 tons
- Buffalo Hydraulic specifications provide analog and digital measurement methods
- Direct and remote mounted pressure gauges with written certification traceable to Bureau of Weights & Measures
Solid test weights offer traditional accuracy:
- Available from 50 micrograms to five tons in all accuracy classes
- ASTM Classes 6 and 7, OIML Class M1, and NIST Class F standards ensure precision
- Cast iron construction provides durability for repeated testing cycles
- Minimal maintenance requirements once procured
Static testing validates the structural capacity of lifting equipment under controlled conditions before workplace deployment.
Which Equipment Is Used for Dynamic Load Testing Applications?
Dynamic load testing equipment applies 110% of rated capacity for a minimum of 1 hour with all mechanisms operated to evaluate performance under working conditions.
Wireless load monitoring systems enable real-time assessment:
- Handle up to 126 simultaneous connections for complex testing scenarios
- Data logging speeds reach 200Hz for comprehensive performance capture
- Significantly cheaper and quicker execution compared to static testing methods
- Real-time feedback allows immediate adjustment during testing procedures
IoT sensors provide continuous monitoring capabilities:
- Collect real-time data on load parameters and equipment performance
- Enable remote monitoring during dynamic testing cycles
- Integrate with cloud-based platforms for data analysis and reporting
- Support predictive maintenance through continuous performance tracking
Advanced load cell technology ensures measurement reliability:
- Provides real-time data with high accuracy for safe load limit verification
- Digital output eliminates analog signal degradation over distance
- Compact dimensions accommodate space-constrained testing environments
- Integration with wireless systems eliminates cable management challenges
Dynamic testing evaluates how lifting equipment performs under operational stress, revealing potential issues that static testing cannot detect. This testing method ensures equipment operates safely within its working load limits during actual lifting operations.
How Do Water Bags and Hydraulic Load Cells Compare for Load Testing?
Water bags and hydraulic load cells represent the two dominant technologies for lifting gear load testing, each offering distinct advantages for specific testing scenarios. Water bags excel in transportability and large-capacity applications, while hydraulic load cells provide superior measurement precision and versatility. The following sections examine the specific benefits and limitations of each technology to guide equipment selection decisions.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Using Water Bags?
Water bags offer several key advantages for load testing applications:
Benefits:
- Proofload water bags are available in sizes ranging from 1 to 100 tons, with tests capable of reaching 1000 tons or more when used with spreaders
- Lightweight design enables easy transport; 100-ton test equipment can be transported by pickup truck
- Canflex turnkey units include safety shackles, master link, fluid transfer fittings, hoses, and valves with minimum 7:1 safety factor
- Low headroom water bags range from 1 to 12.5 tonnes for confined spaces
Limitations:
- Regular cleaning required to remove residual impurities, dirt, and microorganisms to prevent corrosion
- Must protect test bags from sunlight exposure to prevent material degradation
- Drop test required as part of periodic maintenance inspections according to OSHA
- Must stop filling immediately if issues arise during load testing and drain to prevent risks
Water bags provide cost-effective solutions for large-capacity testing with minimal setup complexity, making them ideal for field applications where transportability is essential.
How Do Hydraulic Load Cells Improve the Load Testing Process?
Hydraulic load cells deliver superior measurement accuracy and operational flexibility for load testing applications. Buffalo Hydraulic specifications show measurement of both static and tension loads to within (+/-) 1% accuracy of full scale from 1-1,500 tons capacity.
Key advantages include:
- Analog and digital measurement methods available with compact dimensions
- Direct and remote mounted pressure gauges with written certification options traceable to Bureau of Weights & Measures
- Premium indicator performance achieves 91.66% reliability with 95% confidence when using meters costing USD 15,000 or above, achieving 0.02% stability
Technical considerations:
- Load cells experience material hardening with usage, causing predictable shifts in early calibration cycles
- Thread depth and adapter engagement significantly affect load cell accuracy; loose adapters can cause >0.138% output differences
- Enerpac LH50 example: 5 tons (10,000 lbs) capacity at approximately $2,918
Hydraulic load cells excel in applications requiring precise measurement and real-time monitoring capabilities, making them essential for certification testing where accuracy is paramount. The enhanced precision and reliability justify the higher investment for critical lifting equipment certification processes.

When Should Test Weights Be Used Over Other Load Testing Methods?
Test weights are preferred when precision, stability, and compliance with established standards are paramount. This traditional load testing method offers distinct advantages in controlled environments where accuracy takes precedence over convenience. The following examination details when solid test weights provide superior testing outcomes compared to water bags or hydraulic alternatives.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Solid Test Weights?
Solid test weights provide the most stable and accurate load testing method under controlled conditions. These weights meet rigorous ASTM Classes 6 and 7, OIML Class M1, and NIST Class F standards, ensuring exceptional precision for certification requirements. Cast iron test weights are available from 50 micrograms to five tons across all accuracy classes, offering unmatched versatility for different lifting gear capacities.
Key advantages of solid test weights include:
- Superior accuracy: ASTM-certified weights deliver consistent, traceable results
- Minimal maintenance: Once procured, weights require virtually no ongoing maintenance
- Lower initial cost: Traditional weights cost less upfront than hydraulic systems
- Standards compliance: Meet multiple international calibration standards
- Long-term reliability: Cast iron construction provides decades of accurate service
Primary disadvantages include:
- Poor transportability: Heavy and bulky compared to water bags
- Logistical complexity: Requires cranes or specialized handling equipment for positioning
- Extended setup time: Physical placement and arrangement takes longer than fluid systems
- Storage requirements: Substantial space needed for weight storage between tests
- Limited capacity scaling: Adding capacity requires purchasing additional physical weights
According to industry testing protocols, solid weights excel in laboratory environments and permanent testing facilities where precision outweighs portability concerns. A 2023 Morehouse Load Cell Reliability Study showed traditional weights maintain 0.02% stability when properly certified, making them ideal for calibrating other load testing equipment.
Solid test weights remain the gold standard for applications requiring maximum accuracy and regulatory compliance, despite their transportation and handling limitations. This method bridges traditional testing practices with modern certification requirements, ensuring lifting gear meets the highest safety standards.
How Is Load Testing Equipment Selected for Specific Types of Lifting Gear?
Load testing equipment selection depends on the specific lifting gear type, rated capacity, and industry requirements. The selection process involves matching equipment capabilities to regulatory standards and operational needs.
What Factors Influence the Choice of Load Testing Equipment?
The factors influencing load testing equipment choice are equipment type requirements, industry standards, and environmental conditions. Equipment type determines specific testing requirements under federal regulations.
Overhead and gantry cranes require 1.0 to 1.25 times Working Load Limit (WLL) per 29 CFR 1910.179. Chain and wire rope slings require 2.0 times WLL per ASME B30.9. Rigging hardware requires 2.0 times WLL per ASME B30.26, while spreader beams require 1.25 to 2.0 times WLL per ASME BTH-1. Below-hook devices require 1.0 to 1.25 times WLL per ASME B30.20.
Industry sectors affect equipment choice based on risk profiles. Construction accounts for 43% of crane fatalities, while manufacturing represents 24%. Maritime operations require specialized DNV and ABS certifications for offshore applications.
Environmental conditions impact equipment selection significantly. Dramatic temperature shifts cause metal warping, requiring shielded equipment for outdoor testing. Test loads must remain between 100% and 125% of equipment’s rated capacity per OSHA standards.
How Does the Rated Capacity of Lifting Gear Affect Equipment Selection?
The rated capacity of lifting gear affects equipment selection through matching load testing equipment capacity ranges to specific gear requirements. Different testing equipment types cover distinct capacity ranges with varying precision levels.
Water bags handle capacities from 1 to 110 tonnes, with Proofload specifications allowing tests up to 1,000 tonnes using spreaders. Hydraulic load cells cover 1 to 1,500 tonnes capacity with Buffalo Hydraulic specifications providing ±1% accuracy. Interface Force load pins offer standard ratings between 1.1K lbf and 3.3M lbf (500 kg to 1,500 MT) with custom manufacturing available for specialized applications.
| Equipment Type | Capacity Range | Accuracy | Safety Factor |
| Water Bags | 1-110 tonnes | Standard | 7:1 minimum |
| Hydraulic Load Cells | 1-1,500 tonnes | ±1% | Variable |
| Load Pins | 500 kg-1,500 MT | High precision | Custom |
| Tension Links | 1-500 MT | Standard | 2:1 minimum |
Maximum operating loads should not exceed 80% of maximum test load per OSHA standards. Safety factors vary by equipment type, with chain slings requiring 2.0 times WLL and Canflex water bags maintaining a minimum 7:1 safety factor.
The next section examines best practices for maintaining and calibrating load testing equipment to ensure continued accuracy and compliance.
What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining and Calibrating Load Testing Equipment?
Maintaining and calibrating load testing equipment requires systematic adherence to regulatory standards, manufacturer specifications, and industry best practices. Proper maintenance ensures equipment accuracy, extends service life, and prevents costly failures that compromise safety. Equipment downtime costs average $50,000 per day in industrial operations, making proactive maintenance essential for operational continuity.
The following sections detail specific inspection schedules and address common maintenance challenges with proven solutions for optimal equipment performance.
How Often Should Load Testing Equipment Be Inspected and Calibrated?
Load testing equipment inspection frequency follows a tiered approach based on equipment type and usage conditions. New equipment requires mandatory testing before initial use per OSHA 1919.71. Unit proof tests become mandatory every 4 years thereafter, with additional testing required after major repairs to ensure modifications maintain safety standards.
Daily inspection schedules include:
- Pre-shift inspections by operators before each use
- Visual checks for damage, corrosion, or wear
- Verification of load capacity markings and labels
- Cable and connection integrity assessment
Monthly and annual requirements involve:
- Monthly inspections by competent individuals per OSHA 1910.184
- Annual inspections by qualified personnel representing industry best practice
- Comprehensive 12-month inspections mandated by OSHA requirements
- Documentation per ASME B30.9, B30.20, B30.26, and ANSI Z359 standards
Load cell calibration follows specific protocols using measurement standards traceable to SI through National Metrology Institute (NMI). Annual calibration maintains 0.05% stability in load cells, while severe service conditions require quarterly inspections for slings, rigging hardware, and lifting devices.
What Are Common Maintenance Challenges and Solutions?
Load testing equipment faces multiple environmental and operational challenges requiring targeted solutions. Total combined error from non-linearity and hysteresis remains unavoidable but acceptable when error stays within tolerance specifications.
Temperature-related issues present significant challenges:
- Dramatic temperature shifts cause metal warping
- Shield equipment from direct sunlight exposure
- Implement temperature compensation in electronic systems
- Use materials with stable thermal coefficients
Load cell performance challenges include:
- Extended pressure causes load cell creep affecting long-term measurements
- Allow sufficient stabilization time between measurements
- Account for creep in calibration calculations
- Monitor drift patterns during extended operations
Environmental protection measures address:
- Moisture infiltration through cable entry areas requiring hermetic sealing
- Corrosion from acids or salts disrupting signal integrity
- Vibration interference requiring dampening devices or electronic filtering
- Proper connections critical for signal stability
According to the Morehouse Load Cell Reliability Study (2023), failure rates vary significantly by test point: 5.26% at 10% capacity, 1.75% at 50% capacity, and 1.17% at 100% capacity. Industry standard ‘out-of-box’ failure rates reach 1-2% for some suppliers, while ANYLOAD targets less than 0.01% failure rate through enhanced quality control.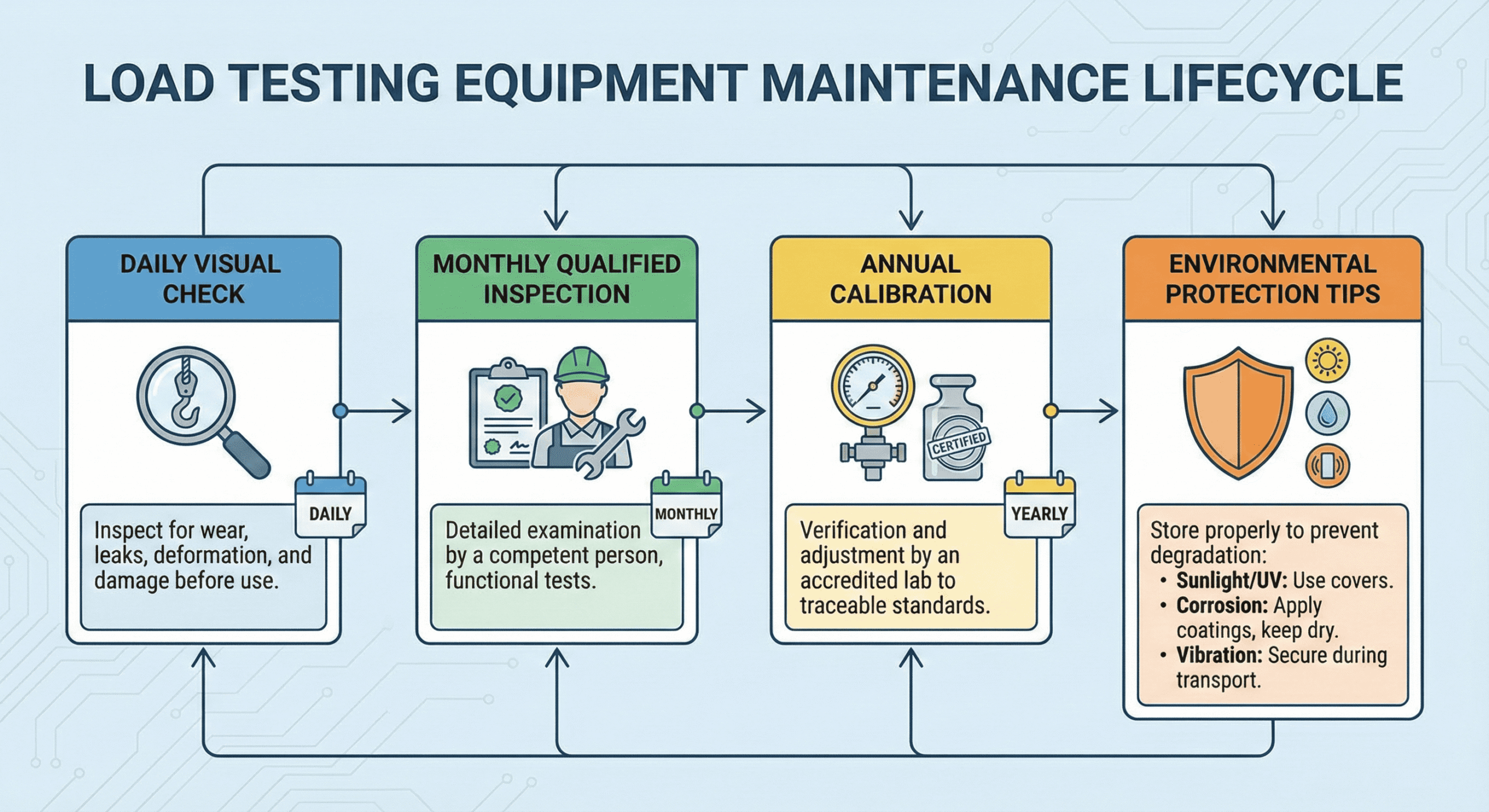
Systematic maintenance protocols prevent most failures while ensuring compliance with safety regulations and optimal equipment performance throughout service life.
How Should You Approach Load Testing Equipment Selection and Certification with a Professional Lifting Equipment Provider?
Approaching load testing equipment selection and certification requires partnering with experienced providers who understand regulatory requirements, equipment capabilities, and industry best practices. Professional lifting equipment providers offer comprehensive services including equipment supply, testing capabilities, certification documentation, and ongoing maintenance support to ensure compliance and safety.
Can Tway Lifting Help With Supplying or Certifying Load Testing Equipment for Lifting Gear?
Tway Lifting can supply and certify load testing equipment for lifting gear applications. Founded in 1945 by Joseph R. Tway, the company operates as America’s premier source for quality American lifting products with comprehensive testing and certification capabilities.
The company maintains hydraulic testing capability for equipment capable of applying tensile loads up to 220,000 lbs. Every sling chain undergoes hydraulic proof load testing as the final quality check of the entire assembly. Every alloy sling chain bears a unique serial number referenced on a Certificate of Test listing chain type, working load, and actual proof load applied.
Tway Lifting provides contract services for manufacturers, engineers, and consumers of non-standard devices, structures, and fabrications. The company operates two Rigging Equipment Superstores in Indianapolis and Fort Wayne, Indiana, with rental equipment including shackles, hoists, slings, and load cells available at daily, weekly, and monthly rates.
Spreader beam rentals range from 2 through 100 tons capacity up to 40 feet in length using the Modulift system. Free local delivery and pick-up are included with all rentals, with nationwide delivery available. The Wire Rope Products Plant is among the few facilities capable of producing heavy lifting gear same-day.
What Are the Key Takeaways About Types of Load Testing Equipment Used for Lifting Gear Certification We Covered?
The key takeaways about load testing equipment types include equipment categories, regulatory requirements, safety statistics, and emerging technologies. Load testing equipment encompasses water bags (1-110 tonnes), hydraulic load cells (1-1,500 tonnes with ±1% accuracy), and solid test weights (ASTM certified) for different applications and capacity requirements.
OSHA 1910.179 and ASME B30 standards mandate load testing before initial use and every 4 years thereafter with test loads 100-125% of rated capacity. According to industry data, 297 total crane-related deaths occurred from 2011-2017 with an average of 42 per year, and men accounted for 293 of 297 fatal injuries.
The Test and Measurement Equipment Market was valued at USD 38.91 billion in 2024. The Load Monitoring System Market reached USD 5.79 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 7.53 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 5.5%. IoT sensors, wireless load monitoring, cloud-based testing platforms, AI-driven optimization, and blockchain digital certification represent emerging technologies transforming the industry.
Proper maintenance including annual calibration, thread engagement verification, and hermetic sealing proves critical for equipment longevity. Equipment selection depends on load application method, transportability, cost, accuracy requirements, and maintenance needs to ensure optimal performance and compliance with safety standards.









